Please configure
Understand WiFi speeds
Learn about WiFi and the factors inside your home that affect the internet speed you'll experience over WiFi.
Check Connection tool
Experiencing slow speeds? Try the Check Connection tool. Learn how to use the Check Connection tool
This tool automatically scans your home connection and diagnose issues. It will then give you recommendations on how to fix or optimise your home network.
It's important to note that speeds can also be affected by external factors such as New Zealand and overseas networks, environmental factors and the location of the server you’re connected to. For Wireless Broadband, factors such as the distance you are from a cell tower, the network capability and the overall use of that cell tower by other consumers can impact the speed experienced.
What's the difference between WiFi and ethernet?
There are two main ways you can connect to the internet:
- Ethernet. This is where you connect an ethernet cable from your modem to your computer. It gives you a stable, faster connection but you'll need to have the cable plugged in whenever you want to connect to the internet.
- WiFi. This lets you connect to the internet without plugging any cables into your device. Data transmits between the modem and your device wirelessly.

Why are my WiFi speeds slower than expected?
WiFi will almost always be slower than if you're connecting via an ethernet cable. There are a few reasons for this:
- Distance from the modem
- The number of devices using the same network
- The WiFi bands
- WiFi interference and obstacles
- Your devices
Find out more about each of these below.
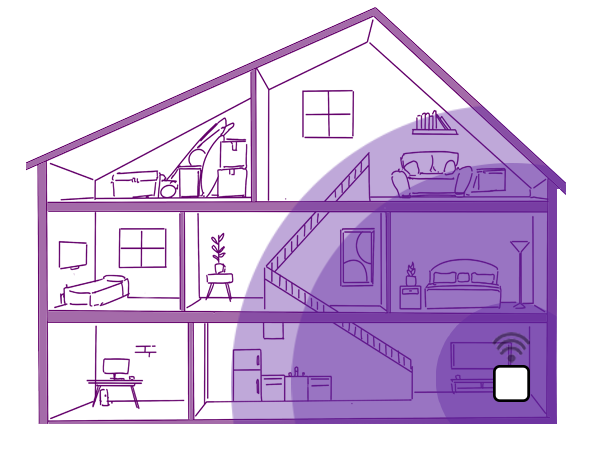
Distance from the modem
The further your device is from your modem, the weaker the WiFi signal will be. If you have a big house you might find there are places where your WiFi coverage has fewer signal bars, or dead spots where it can't quite reach.
If this happens, consider expanding your WiFi coverage. You can do that by installing a WiFi device like the Spark Smart Mesh 2.
The number of devices using the same network
Many households have a number of devices such as mobile phones and laptops connecting to the internet over WiFi at the same time. Some households also have smart devices such as TVs, security cameras, voice assistants, smart light bulbs, smart plugs and vacuum cleaners connected to WiFi.
If you use the internet on a single device, it can access the majority of the speed that's available. When multiple devices use the internet at the same time, your available speed is shared between them.
If your household uses many devices at the same time, consider upgrading your Fibre plan to one with a faster speed. Change broadband plan
You'll need to check your modem is compatible with the higher speed. Check modem compatibility

WiFi bands
Most newer modems have two WiFi bands: 2.4GHz or 5GHz. When you looked for your WiFi name on your device, you may have noticed two options with a similar name.
The 2.4GHz band provides WiFi coverage to a larger area but has lower speeds. The 5GHz band provides faster speeds but to a smaller area. Some devices are only able to connect to 2.4GHz.
Newer modems such as the Spark Smart Modems have band steering. This means your device will automatically connect to the appropriate WiFi band based on your distance from the modem.
If you're using a different kind of modem, you'll need to select the most appropriate band yourself when connecting to the internet over WiFi. If you need WiFi in more rooms of your house, select 2.4GHz. If you have a smaller, open plan house, 5GHz may provide a better WiFi experience if your device is able to connect to it.

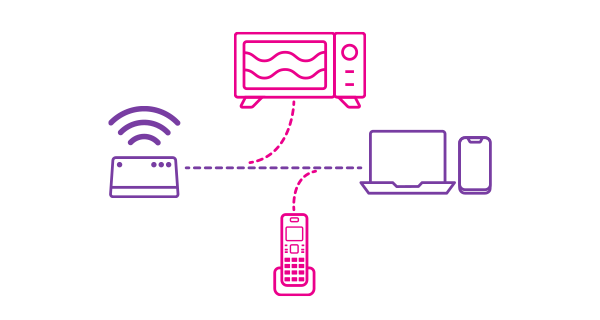
WiFi interference and obstacles
Your WiFi network can be affected by interference. Some factors in your house that can cause this are:
- Physical barriers. This is one of the most likely reasons for the WiFi signal being unable to reach your device. Concrete or metal barriers like walls, floors, TVs or fish tanks can diminish or block the WiFi signal.
- Other devices in use. Most microwaves operate on the 2.4Ghz spectrum. This is the same as a lot of wireless devices, so your microwave may interfere with your WiFi while it's in use. Other household devices such as cordless phones, refrigerators and baby monitors may also interfere with your WiFi.
Your devices
Older mobile phones, computers and other devices may not be compatible with higher speeds. Check with your device manufacturer to see what the maximum WiFi speeds they'll support are.
Viruses or firewalls may also be slowing your device speed down. Keep your anti-virus software up to date. Check your firewall settings to see if there are any rules or configurations that are slowing down your internet.
What can I do to improve my speeds?
Some things you can try:
- Use the Check Connection tool in the Spark app to find and fix problems with your in-home setup. Find out how to check your connection
- Look at the location of your modem. Place it off the ground in a central location, away from items that cause interference.
- For Fibre broadband, check that the ethernet cable that connects your fibre box (ONT) to your modem is Cat 5e or above. above. This is because ethernet cables that are Cat 5 or below limit the maximum speed to 100Mbps or below. Most ethernet cables have the category printed along the cable.
- If you want a faster and more stable connection, plug devices such as TVs and desktop computers into your modem using an ethernet cable. Check that the cable is Cat 5e or above. This may not be possible on some devices such as mobile phones, and you wont be able to move about with your device.
- Check your modem is compatible with your broadband plan's speed, especially if you have an older modem. Not all modems can deliver higher speeds. Check modem compatibility
- Check your device. If you're connecting an older device to the internet, it might not be compatible with higher speeds. Check with your device's manufacturer to see what speeds your device is capable of.
- Expand your coverage. If your WiFi isn’t reaching the far corners of your home, a Spark Smart Mesh 2 may help expand your WiFi signal. Installing a WiFi mesh or extender will allow devices further away from your modem to connect to the internet, but it may not improve the speed if you’re on a slower plan or if your WiFi network is affected by factors listed above. Find out more about Smart Mesh 2
- If you're rewiring your home, consider installing Cat 6 cabling and a star wiring configuration. Cat 6 cabling can process more data than Cat 5e cabling.
